Working with Images in Graphic Converter
Changing the View
Size of Your Graphic
In Graphics Converter there is a tool that allows you to change the magnification
of the image that you are working on. This is very handy if you are working
on a small image and need to see details, or if you are working on a large
graphic and need to reduce it so that it will fit on the screen. This does
not change the actual size of the graphic, only your view of it while you
are working.
 Click on the zoom tool.
Click on the zoom tool.- To enlarge the view of your graphic, click on the canvas. It will immediately
magnify the image. Keep clicking until you are satisfied with the size of
your image.
- To reduce the view of your graphic, hold down the OPTION key and click
on the canvas.
- To return to the actual image size, from the Picture menu select
Zoom and then View as 100%.
Drawing and Deleting Graphics
Drawing Freehand
 Select the pencil
tool.
Select the pencil
tool.- Click on the foreground color tool in the toolbox and select the desired
color.
- Click on the pen size tool in the toolbox and select the desired pen
width.
- On the canvas, click on the spot where you would like to start drawing
and drag the mouse to draw freehand.
Drawing Lines
 Select the line tool.
Select the line tool.- Click on the foreground color tool in the toolbox and select the desired
color.
- Click on the pen size tool in the toolbox and select the desired thickness
of the line.
- On the canvas, click on the spot where you would like the line to begin
and drag to where you would like it to end. (If you want your line to
be perfectly horizontal or vertical, hold down the SHIFT key as you drag
the mouse.)
Drawing Shapes
There are three different shape tools in Graphic Converter: the rectangle,
the rounded rectangle, and the ellipse (ovals and circles).
To draw a rectangle or square:
 Select the appropriate
rectangle tool.
Select the appropriate
rectangle tool.- Click on the foreground color tool in the toolbox and select the desired
color.
- Click on the pen size tool in the toolbox and select the desired thickness
of the line.
- Click and drag on the canvas until your rectangle is the correct size.
- To draw a square, hold down the SHIFT key on your keyboard while you
click and drag.
To draw a rounded rectangle or square:
 Select the appropriate
rounded rectangle tool.
Select the appropriate
rounded rectangle tool.- Click on the foreground color tool in the toolbox and select the desired
color.
- Click on the pen size tool in the toolbox and select the desired thickness
of the line.
- Click and drag on the canvas until your rectangle is the correct size.
- To draw a rounded square, hold down the SHIFT key on your keyboard while
you click and drag.
To draw an ellipse or circle:
 Select the appropriate
ellipse tool.
Select the appropriate
ellipse tool.- Click on the foreground color tool in the toolbox and select the desired
color.
- Click on the pen size tool in the toolbox and select the desired thickness
of the line.
- Click and drag on the canvas until your ellipse is the correct size.
- To draw a circle, hold down the SHIFT key on your keyboard while you
click and drag.
Adding Text to Your Graphic
 Double-click on the
text tool to open its dialog box.
Double-click on the
text tool to open its dialog box.- Select the desired font and size of the text in the pull-down menus.
- Select the desired style(s) for the text.
- Click OK to close the dialog box.
- On the canvas, click on the spot where you would like the text to begin.
A dashed box will appear, indicating where your text will be placed.
- Type in the desired text.
 To resize the text box,
move the mouse to a corner of the box until you see a double-arrow, click
and drag on the corner to adjust.
To resize the text box,
move the mouse to a corner of the box until you see a double-arrow, click
and drag on the corner to adjust.
 To move the text box,
move the mouse over the text box so that you see a hand, click and drag
to move.
To move the text box,
move the mouse over the text box so that you see a hand, click and drag
to move.
Note: You can edit the text and adjust the size of the text
box as long as you don't click anywhere else on the picture.
Deleting
There are two ways of deleting in Graphic Converter: selecting an area
and deleting the area or dragging the mouse over where you would like to
delete. One method will be more useful than the other, depending on what
you're doing.
Deleting an area
 Click on the
appropriate selection tool to select the area you want to delete most
closely.
Click on the
appropriate selection tool to select the area you want to delete most
closely.- Select the area you want to delete. A dashed outline will indicate the
area you've selected.
- Hit the DELETE key on your keyboard.
Deleting more precisely
 Double-click on
the eraser tool to open its dialog box.
Double-click on
the eraser tool to open its dialog box.- Select the desired shape and then size of the eraser and click OK.
- On the canvas, click on the spot that you would like to delete. If the
section you want to delete is larger than the size of the eraser, you
can also click and drag on the canvas until you have deleted everything.
Editing Images
Graphic Converter has many image editing features. The first set of features
is listed under the Edit menu. These features allow you to copy, paste,
crop, or trim an image. The second set of features, listed under the Picture
menu, lets you change the size, proportions, orientation, or resolution of
an image. The last set of features, listed under the Effects menu,
can be used to perform various filtering, smoothing, or sharpening effects
on an image to enhance or obscure its quality.
To begin editing an image:
- From the File menu select Open.
- On the bottom of the window that appears, make sure the Filter is
set to All Available.
- Select the file you wish to edit, then click Open. To open multiple
images, hold down the Apple key while selecting images.
To Copy an image into
memory:
- From the Edit menu choose Select All
- From the Edit menu choose Copy.
- The image will be stored in memory. You can then paste the image into
a Word document, web page, Excel spreadsheet, or any other file by choosing
Paste from the Edit menu in those applications.
To Crop or Trim an image:
 Choose either
the Lasso or Select tool from the Toolbar.
Choose either
the Lasso or Select tool from the Toolbar. - Enclose the portion of the image that you would like to trim. The portion
you want to trim away should be located outside the dotted select line.
- From the Edit menu choose Trim Selection. The trimmed
portion will appear in a new window.
Note: You can also select Edit > Smart Trim if you
want Graphic Converter to crop the image automatically to get rid
of excess white borders.
To Resize an image:
To change the size of an image relative to its current size:
- From the Picture menu choose Size and then Scale.
- In the Dimension section of the Scale dialog box, make
sure that Width and Height are set to Percent.
- Type in the percent value you want the image to change by. For example,
a value of "0.5" will shrink the width or height by one-half while a
value of "3.0" will triple it.
- If you wish to maintain the original image's proportions, make sure
the Keep Proportions box is checked. If you want to change
the width and height of the image separately, leave the Keep Proportions box
unchecked.
- Click OK.
To change the exact size of an image by actual dimensions:
- To find the exact dimensions of your image, from the Picture menu
choose Show Information.
- An Information window will appear.
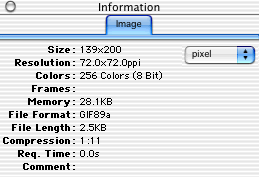
- The first number (in this case 139) is the exact width of the image
in pixels; the second number (200) is its height.
- From the Picture menu, choose Size and then Scale.
- In the Size section of the Scale dialog box,
choose either pixel, inch or cm.
- In the Width or Height fields, type a number for the
desired change.
- If you wish to maintain the original image's proportions, make sure
the Keep Proportions box is checked. If you want to shrink
the image by only one dimension, leave the Keep Proportions box
unchecked.
- Click OK.
Note: To undo size changes from the Edit menu choose Undo:Scale.
Once you perform another operation or save the file, however, the changes
cannot be undone. It is a good idea to keep
backup files in case you accidentally change an image permanently.
To change the Orientation
of an image:
To rotate the image by a certain degree:
- From the Picture menu choose Rotate
- Select an angle by which to rotate the image.
- You can use Other Value with Line to rotate at an angle specified
by a line drawn on the image
- You can type in a specified angle of rotation under Other Value....
To flip the image across an axis:
- From the Picture menu choose Mirror
- Select an axis on which to flip the image
To change the Resolution
of an image:
- From the Picture menu choose Resolution
- Enter the desired resolution (generally 150-250 for images that you
will print out and 72 for images that will be displayed on a screen)
To change the Appearance
of an image:
Brightness and contrast can be altered to adjust the shading of an image.
- From the Picture menu choose Brightness/Contrast
- Adjust these values according to the desired appearance.
Note: You can also use Graphic Converter's various filtering
effects to change the appearance of an image. These features are listed
in the Effects menu. One of the most useful features is one that
sharpens the edges of an image, making most images look cleaner and
of higher resolution.
From the Effects menu choose Sharpen Edges and choose
a value. The image will appear sharper than before.
Converting Images among File Formats
Just like word processing documents, images can exist in a variety of file
formats. Some computers can read one type of format, while other computers
may read a different format. When editing images, it is important to save
images in a file format that can be read by the intended computer or program.
For example, Macintosh computers typically use the PICT format for saving
image files. PCs generally use the BMP image format. If you want the image
to be viewable on a PC, you will want to use Graphic Converter to convert
it from PICT to BMP.
Different programs can also use different file formats. Although Microsoft
Word can read PICT files, Internet Explorer and Firefox read only JPEG (.jpg), GIF (.gif) or PNG (.png) images files. Again,
you can use Graphic Converter to convert images so that other programs can
read your image files.
There are two methods for converting files to different formats, depending
on the number of images you wish to convert.
If you want to convert a single image file
- Open Graphic Converter.
- From the File menu, choose Open.
- In the Open: GraphicConverter dialog box, make sure the Filter is set
to All Available.
- Find and select the file you wish to convert, then click Open.
If you get a pop-up dialog box, select Don't Change.
- Once the file is open, go to the File menu and select Save
As.
- From the Format pull-down menu, select the desired file format. Make
sure that the file extension of the file name matches the format selected.
- Click Save. Depending on the file format chosen, more dialog
boxes may pop up. Select desired preferences, then click OK.
If you want to convert more than one or two image files, you can convert
them all at once using the Graphic Converter's batch conversion feature.
- Open Graphic Converter.
- From the File menu, choose Convert.
- A Convert window will appear.
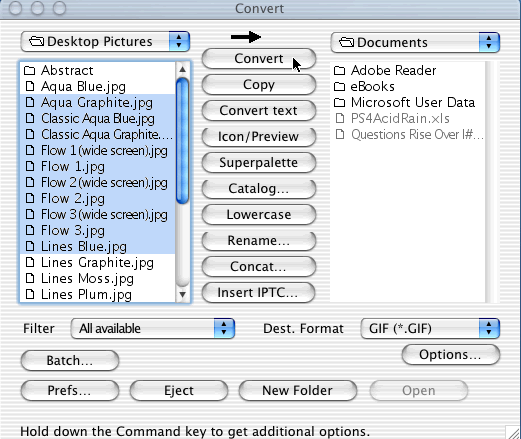
- On the left side of the window, double-click on folders to browse to
the image files you want to convert.
- Make sure the Filter is set to All Available.
- Select the image files you want to convert by clicking on them once
while holding down the Apple key. You can also deselect a file the same
way.
- On the right side of the screen, browse to the folder you want to save
the converted images to (you can also click the New Folder button
to create a folder for saving the converted images).
- Select the desired file format from the Dest. Format pull-down
menu
- Click Convert.
- The selected files in the left box will be converted and copied to the
folder indicated in the right box.
Modified from tutorial created by Heather Woods for Wellesley College
 Click on the zoom tool.
Click on the zoom tool.
